Top of Page
- Links to move inside this page.
- HOME
- Investor Relations
- ESG Initiatives
- Environment
Environment
Policy for environmental initiatives
In order to continuously realize the IIJ Group's business philosophy and to achieve long-term sustainable growth, IIJ Group recognizes the importance of taking initiatives in the reduction of environmental impact on the society as a whole through business activities that comply with environmental laws and regulations and take the global environment into account.
As the first commercial Internet service provider in Japan, IIJ has created the Internet infrastructure in Japan and has been providing Internet connectivity services. Social and economic activities are obviously more efficient than they were about 30 years ago with the use of internet-based services and applications. IIJ Group will continue to stably provide highly reliable services that support the networked society such as the Internet and cloud computing services thereby contributing to further improving the efficiency of social activities and reducing the environmental impact on the entire society.
Meanwhile, the use of electricity is essential in providing these services, and the IIJ Group is required to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and realize the carbon neutrality of data centers where a large amount of electricity is consumed.
Additionally, to make its data center a reference model for carbon neutral data centers, IIJ will pursue diverse initiatives by increasing renewable energy as a percentage of its total energy use toward 2030 and setting targets for increasing energy efficiency. In addition, IIJ Group will make an effort to promote procurement activities that take into consideration the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions throughout the supply chain when procuring equipment and services necessary for the provision of its services from partner companies.
IIJ has established the "Sustainability Committee", chaired by the President, to promote these activities as a company-wide initiative, and will implement PDCA activities to reduce the environmental impact. IIJ will disclose sufficient environmental information to its stakeholders.
In light of the purpose of the Corporate Governance Code revised in June 2021, IIJ will enhance environmental disclosure based on the TCFD framework etc. in accordance with the above policy.
Improvements in energy efficiency
In recent years, the problem of climate change has become a material issue of urgency that the international community has to address, and, for example, companies are being required to further reduce greenhouse gas emissions. As energy sources account for a large proportion of the CO2 emissions in many countries, it is important to reduce unnecessary energy use and strive toward more efficient use.
IIJ is actively promoting efforts to cut our energy consumption at data centers in particular, because they are said to account for 2% of all the electricity consumed in the world. In addition, the Internet's characteristic of reducing the movement of people and things is considered to be one way of helping to substantially improve energy efficiency throughout society as a whole.
Initiatives at Matsue Data Center Park

In 2011, IIJ opened Matsue Data Center Park ("Matsue DCP"), Japan's first modular data center with an outside air cooling system. Matsue DCP has adopted a container-unit modular architecture that integrates IT equipment and air conditioning as a module in a container, thereby enabling a much shorter construction period and flexible reconfiguration. In addition, each modular IT container uses IZmo to automatically select the operating mode appropriate for the temperature and humidity, thereby saving considerable amounts of energy.
Furthermore, the data center received ISO 14001 certification (environmental management systems) in 2013 to continuously promote environmental improvement activities, such as energy saving at data centers, throughout the organization.
In addition, IIJ made a joint proposal with Matsue City as a private sector provider of data center when applying for the Ministry of the Environment's Decarbonization Leading Areas, and Matsue City was selected as a Decarbonization Leading Area in April 2023.
IZmo IT module

Air conditioning systems in common data centers require large amounts of electricity to combat the heat emitted from IT equipment. IZmo units, Matsue DCP's IT modules, have adopted the first outdoor air cooling system for a commercial data center so as to use compressors and chillers less frequently, thereby significantly reducing electricity consumption.
In addition, in contrast to conventional data centers that require large quantities of packaging and protective materials when carrying in and installing servers, IZmo units can be transported to a data center with servers pre-installed, which contributes to reducing not only packaging materials, but also CO2 emissions during transportation.
Realization of energy-saving
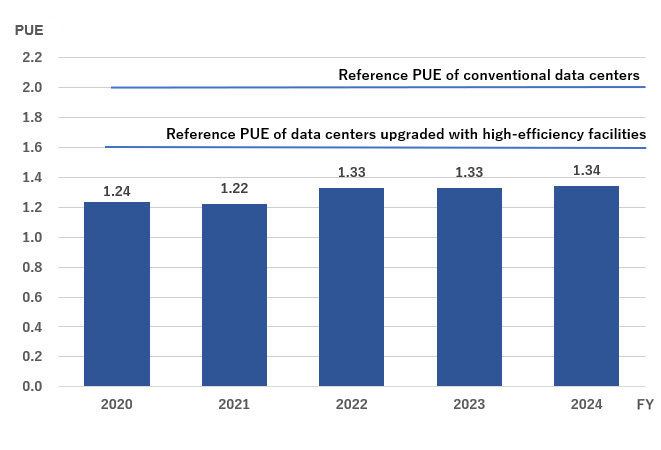
Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) is a metric that shows how efficiently electricity is used at a data center. It is calculated by dividing the electricity that an entire data center consumes by the electricity that the IT equipment there consumes. The closer to 1.0 the metric is, the more efficiently the data center uses power. In Japan, the metric is 2.0 for conventional data centers and 1.6 for newer data centers with highly efficient facilities. In comparison, Matsue DCP has achieved figures in the 1.3 range. Additionally, IIJ introduced electricity virtually derived from renewable energy in February 2022 and installed solar panels on the rooftop of its administration building in 2023. This has made it possible for 100% of the energy we use to be from renewable source of energy.
Annual Average PUE of Matsue DCP
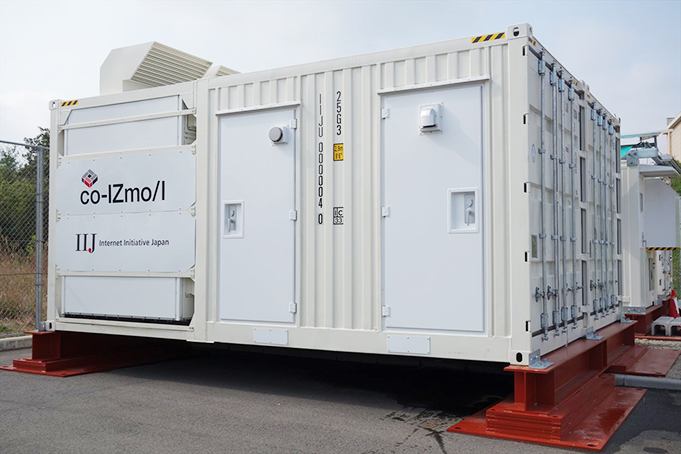
co-IZmo/I, a container-unit modular data center developed in 2013, adopted an indirect outside air cooling system so as to achieve high energy-saving performance even in an environment where the air quality is poor, such as air with a high grit, dust, and salt content. As such, IIJ foresees it spreading to a wide range of regions.
co-IZmo/I

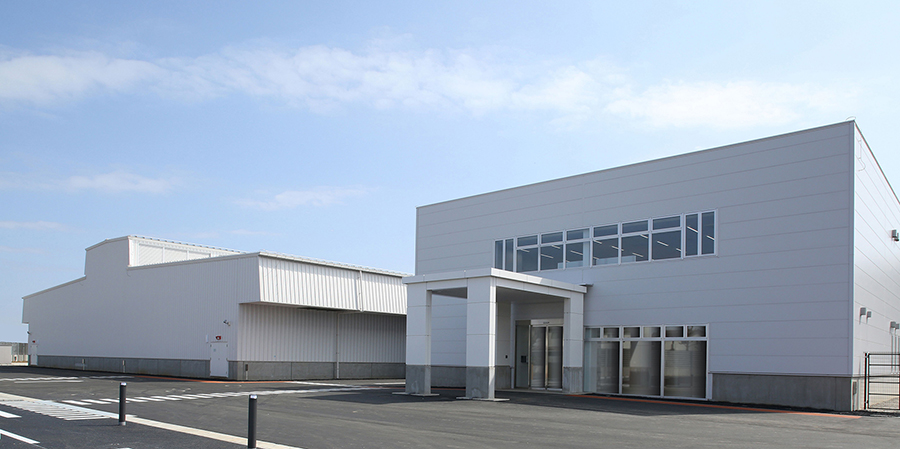
Initiatives at Shiroi Data Center Campus
In May 2019, to accommodate the large-scale demand accompanying increases in digital data expected due to the spread of 5G, IoT, and AI and etc., IIJ started operating the Shiroi Data Center Campus("Shiroi DCC") in Shiroi, Chiba Prefecture with the help of knowledge gained at Matsue DCP. This data center campus adopted a system-module construction method that enables a larger-scale modular architecture, thereby systematizing and streamlining construction and production processes prior to construction work.
- the air-conditioning modules (Energy-saving initiatives—outside-air cooling, bus ducts, three-phase four-wire UPS)
- Shiroi Data Center Campus
Shiroi Data Center Campus

Peak cut / peak shift of electric power by storage batteries
High-capacity lithium-ion batteries installed
at the Shiroi DCC

At the Shiroi DCC, the lithium-ion storage batteries installed as a power supply during emergencies are also used during normal operations to promote load shifting and peak shaving in power demand.
Since their introduction in 2019, IIJ has verified their use in equalizing power for summer air conditioning and their peak shaving and load shifting performance. As a result, in August - the annual peak period - we measured a peak shaving effect of 10.8% of the total Shiroi DCC power demand.
Estimated reduction in electricity consumption achieved with system cloud IIJ GIO
In 2009, IIJ launched IIJ GIO, cloud service, and has provided many corporate customers with this service. IIJ GIO uses energy-efficient data centers, including Shiroi DCC and Matsue DCP, as its infrastructure and consolidates IT resources more efficiently using massive servers and storage equipment, thereby significantly reducing electricity consumption.
The entire service infrastructure consumes approximately 99,000 MWh of electricity per year, estimated to be an approximately 40% reduction (amount of electricity consumed by about 15,000 general households (*)), compared to the situation where everything is in an on-premises environment. Going forward, IIJ will contribute to reducing CO2 emissions by pursuing improvements to IIJ GIO's energy efficiency and helping cut the electricity that society consumes when using IT.
- (*)Calculated by assuming that the average household consumes 4,175 kWh of electricity annually based on the "FY2021 Statistical Survey of CO2 Emissions from the Household Sector" by the Ministry of the Environment of Japan
Joint Crediting Mechanism: Energy-saving data center project in Laos
First energy-efficient data center in Laos

The Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) is a system to help reduce greenhouse gases (GHGs) by: spreading outstanding low-carbon technologies, products, systems, services, and infrastructures; promoting measures in developing countries; quantitatively evaluating how much Japan has contributed to reducing and absorbing GHGs through these activities; and utilizing evaluation results to achieve Japan's GHG reduction targets. Using this system, the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) contracted IIJ, Toyota Tsusho, and Mitsubishi UFJ Morgan Stanley Securities for a demonstration project aimed at verifying how effectively greenhouse gases can be reduced with the modular data center construction and operation technologies. This project involved installing co-IZmo/I, a modular data center, in Vientiane, Laos and verifying operations appropriate for the country's environment and greenhouse gas reduction effects. At the same time, the project contributed to building the country's first state-owned energy efficient data center, which will plays a central role in the country's low-carbon growth model in field of IT.
In January 2019, this JCM project was issued credits (207t in total). This was the first time ever that a NEDO demonstration project had been issued credits in Laos since JCM was launched between Japan and Laos in 2013.
Initiatives through products and services
Remote access to reduce the movement of people and things
As working environments are rapidly becoming digital, as represented by telecommuting and web/video conferencing, the IIJ Group provides companies with a "digital workplace," a comfortable and productive digital space.
The VPN service IIJ Flex Mobility Service, with its low latency and stable connections, prevents communication interruptions even in places with unstable mobile connections. This service is just a sample of IIJ offers to increase productivity and enhance corporate value.
IIJ also contributes to climate change mitigation by promoting digital workplaces through our infrastructure and reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with the movement of people and goods.
Providing support ranging from the visualization of energy usage to the development of CO2 emissions targets
Smart meters are available in two types: "A-route" smart meters retrieve data every 30 minutes for use by general electric utilities to calculate electricity bills. In contrast, "B-route" meters retrieve electric usage data in virtually real-time. IIJ offers the authentication devices and services needed in B-route applications.
In addition, IIJ provides the Energy-saving IoT Package, a one-stop solution that provides the IoT sensors, networks, and visualization platforms needed to visualize energy usage as a monthly fee-based service and support the calculation of CO2 emissions and the development of reduction targets to help the manufacturing industry realize carbon neutrality.
- IIJ High Voltage Smart Metering Service for B Route
- IIJ and Mitsubishi HC Capital collaborate on the visualization solution supporting businesses promotion of DX, and it has started to offer an Energy-saving IoT Package that supports carbon neutrality in the manufacturing industry (Japanese text only)
Utilization of renewable energy
As well as saving energy, IIJ must choose energy sources that emit less CO2 so as to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. As IIJ consumes a large amount of electricity for our operations, including data centers, IIJ recognizes the need to address this issue and is considering ways to covert energy.
Initiatives at Matsue Data Center Park
In February 2022, Matsue DCP began using electricity virtually derived from renewable energy (renewables)(*1) at Site 1. In March 2023, the photovoltaic power generation panels installed on the rooftop of the administrative building on the premises of DCP began operating. The installed capacity of the photovoltaic power generation panels is nearly 7% of electricity used in the Matsue DCP server building. Annual power generation is estimated to be nearly 340 MWh. Currently, Site 2 has also completed its introduction of renewables-derived electricity. As a result of these efforts, 100% of the electricity used by Matsue DCP is from renewables.
Moreover, the electricity to be introduced this time uses FIT non-fossil certificate with tracking (*2) and meets RE100 (*3).
- (*1)Electricity that is regarded as substantially 100% renewable electricity and emitting zeroCO2 by adding the environmental value certificate to the power source of electricity companies.
- (*2)Non-fossil certificate is a certificate of the environmental value as non-fossil energy (effect of the reduction of CO2emissions, etc.) for the electricity generated from non-fossil energy such as renewable energy and nuclear energy, and is issued through the Non-fossil Value Trading Market established in May 2018.
- (*3)RE100 (Renewable Energy 100%) is an international initiative aiming to procure energy consumed in business activities from 100% renewable energy.
Initiatives at Shiroi Data Center Campus
The solar system at Shiroi Data Center Campus

The Shiroi Data Center Campus is building a facility for an on-site megasite solar power generation system and it procures electricity from off-site power generation facilities. In April 2023, it became a member of Japan Electric Power Exchange's non-fossil value transactions which made it possible to purchase and mediate FIT non-fossil certificates.(*) By doing so, the Campus provides renewables-derived electricity using FIT non-fossil certificates to customers upon request. Efforts such as these to realize carbon neutrality will continue.
- (*)A certificate of environmental value of non-fossil electric power that is purchased through the FIT (feed-in tariff) system
End of the page.
